目录
1. 了解AuthenticationManager
1.1 ProviderManager
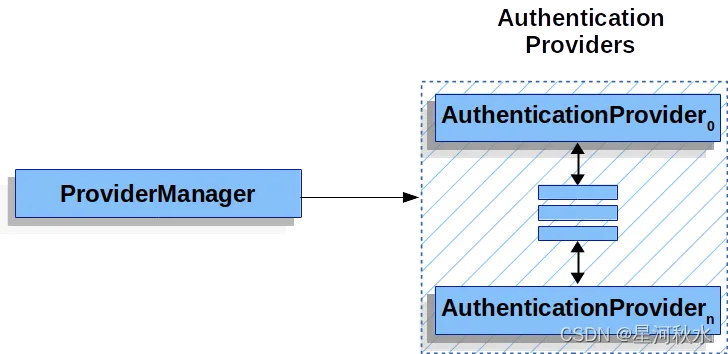
ProviderManager管理了一个AuthenticationProvider列表,每个AuthenticationProvider都是一个认证器
ProviderManager 相当于代理了多个 AuthenticationProvider,他们的关系如下图:
1.2 AuthenticationProvider
javapublic interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> var1);
}
AuthenticationProvider
- authenticate方法来验证,就是验证用户身份
- supports用来判断当前AuthenicationProvider是否对应支持Authentication
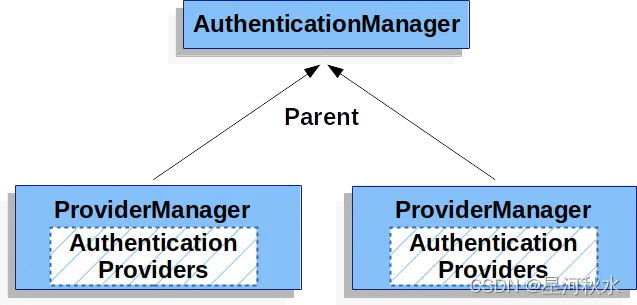
1.3 Parent
- 一个ProviderManager管理多个AuthenticationPorvider
- 每一个ProviderManager可以配置一个parent
- 如果当前的 ProviderManager 中认证失败了,还可以去它的 parent 中继续执行认证(一般还是ProviderManager)
AuthenticationManager 的初始化会分为两块,
一个全局的 AuthenticationManager,也就是 parent,另一个则是局部的 AuthenticationManager。
先给大家一个结论,一个系统中,我们可以配置多个 HttpSecurity(参见Spring Security 竟然可以同时存在多个过滤器链?),而每一个 HttpSecurity 都有一个对应的 AuthenticationManager 实例(局部 AuthenticationManager),这些局部的 AuthenticationManager 实例都有一个共同的 parent,那就是全局的 AuthenticationManager。
2. 源码分析
AuthenticationManagerBuilder 源码比较长,我们来看几个关键的方法
javapublic class AuthenticationManagerBuilder
extends
AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder<AuthenticationManager, AuthenticationManagerBuilder>
implements ProviderManagerBuilder<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> {
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) {
super(objectPostProcessor, true);
}
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder parentAuthenticationManager(
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
if (authenticationManager instanceof ProviderManager) {
eraseCredentials(((ProviderManager) authenticationManager)
.isEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication());
}
this.parentAuthenticationManager = authenticationManager;
return this;
}
public InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> inMemoryAuthentication()
throws Exception {
return apply(new InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<>());
}
public JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> jdbcAuthentication()
throws Exception {
return apply(new JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<>());
}
public <T extends UserDetailsService> DaoAuthenticationConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder, T> userDetailsService(
T userDetailsService) throws Exception {
this.defaultUserDetailsService = userDetailsService;
return apply(new DaoAuthenticationConfigurer<>(
userDetailsService));
}
@Override
protected ProviderManager performBuild() throws Exception {
if (!isConfigured()) {
logger.debug("No authenticationProviders and no parentAuthenticationManager defined. Returning null.");
return null;
}
ProviderManager providerManager = new ProviderManager(authenticationProviders,
parentAuthenticationManager);
if (eraseCredentials != null) {
providerManager.setEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication(eraseCredentials);
}
if (eventPublisher != null) {
providerManager.setAuthenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);
}
providerManager = postProcess(providerManager);
return providerManager;
}
}
步骤分析:
- 1.首先,我们调用parentAuthenticationManager 给AuthenticationManager 设置parent
- 2.inMemoryAuthentication、jdbcAuthentication 以及 userDetailsService 几个方法是配置数据源
- 3.performBuild方法,根据AuthenticationManagerBuilder构建AuthenticationManager
构建ProviderManager,一方面传入authenticationProviders(就是ProviderManager 管理的所有AuthenticationProvider),另一方面传入ProviderManager 的 parent(其实也是一个 ProviderManager)
2.1初始化
AuthenticationConfiguration ,这个类可以当做
java@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(ObjectPostProcessorConfiguration.class)
public class AuthenticationConfiguration {
@Bean
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder(
ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor, ApplicationContext context) {
LazyPasswordEncoder defaultPasswordEncoder = new LazyPasswordEncoder(context);
AuthenticationEventPublisher authenticationEventPublisher = getBeanOrNull(context, AuthenticationEventPublisher.class);
DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder result = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(objectPostProcessor, defaultPasswordEncoder);
if (authenticationEventPublisher != null) {
result.authenticationEventPublisher(authenticationEventPublisher);
}
return result;
}
@Bean
public static GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter enableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(
ApplicationContext context) {
return new EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(context);
}
@Bean
public static InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer initializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {
return new InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer(context);
}
@Bean
public static InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer initializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {
return new InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer(context);
}
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
if (this.authenticationManagerInitialized) {
return this.authenticationManager;
}
AuthenticationManagerBuilder authBuilder = this.applicationContext.getBean(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
if (this.buildingAuthenticationManager.getAndSet(true)) {
return new AuthenticationManagerDelegator(authBuilder);
}
for (GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter config : globalAuthConfigurers) {
authBuilder.apply(config);
}
authenticationManager = authBuilder.build();
if (authenticationManager == null) {
authenticationManager = getAuthenticationManagerBean();
}
this.authenticationManagerInitialized = true;
return authenticationManager;
}
@Autowired
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Autowired
public void setObjectPostProcessor(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) {
this.objectPostProcessor = objectPostProcessor;
}
private static class EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer extends
GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter {
private final ApplicationContext context;
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer.class);
EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public void init(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {
Map<String, Object> beansWithAnnotation = context
.getBeansWithAnnotation(EnableGlobalAuthentication.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly initializing " + beansWithAnnotation);
}
}
}
}
一言以蔽之,AuthenticationConfiguration 中的配置有没有用上,全看开发者有没有重写 configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) 方法,重写了,就用 localConfigureAuthenticationBldr 来构建 parent 级别的 AuthenticationManager,没重写,就用 AuthenticationConfiguration 中的方法来构建。
本文作者:xiech
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!